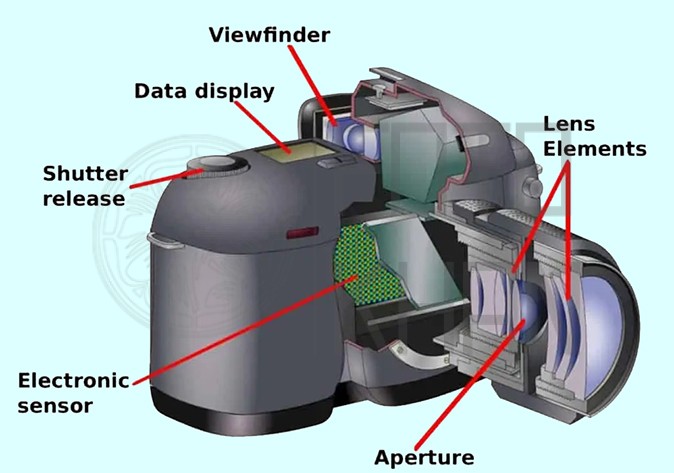
Understanding the key components of a camera is fundamental for beginners looking to dive into the world of photography. Here, we’ll explore three crucial aspects: lenses, sensors, and camera settings, and offer tips to help beginners navigate these critical elements.
1. Lenses:
Lenses are the eyes of your camera, and choosing the right one can significantly impact your photography. Here are some lens-related tips for beginners:
a. Prime vs. Zoom Lenses: Prime lenses have a fixed focal length, making them excellent for portraits and low-light situations. Zoom lenses offer versatility, allowing you to zoom in and out, making them ideal for various shooting scenarios.
b. Aperture: Understand aperture settings (measured in f-stops) and their impact on depth of field and light intake. Lower f-stop numbers (e.g., f/1.8) create a shallow depth of field with blurred backgrounds, while higher f-stop numbers (e.g., f/11) increase depth of field and provide sharpness throughout the frame.
c. Lens Compatibility: Check compatibility with your camera body. Not all lenses fit all cameras, so ensure your chosen lens works with your camera’s mount.
2. Sensors:
The camera sensor is where the magic happens, as it captures the light and transforms it into an image. Understanding sensor size and type is essential:
a. Sensor Size: Larger sensors, like full-frame sensors, generally produce better image quality, especially in low light. However, they often come with a higher price tag. Crop sensors are more budget-friendly and suitable for beginners.
b. Sensor Types: Two common sensor types are CCD (Charged Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor). CMOS sensors are more prevalent in modern cameras due to their superior performance and energy efficiency.
3. Camera Settings:
Learning to navigate your camera’s settings is crucial for capturing the best possible shots. Here are some tips:
a. Shooting Modes: Familiarize yourself with your camera’s shooting modes. Most cameras have automatic and semi-automatic modes, such as aperture priority (A/Av) and shutter priority (S/Tv). These modes help you control specific settings while the camera handles others.
b. ISO: ISO determines your camera’s sensitivity to light. Low ISO values (e.g., 100) are suitable for bright conditions, while higher ISO settings (e.g., 800-3200) are for low-light situations. Be cautious with high ISO, as it can introduce noise (graininess) into your images.
c. Exposure Triangle: Master the exposure triangle, which consists of aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. Understanding how these settings interact is vital for achieving proper exposure and creative control.
d. White Balance: Adjust white balance settings to ensure accurate colors in various lighting conditions. Common presets include daylight, cloudy, and tungsten.
e. Focus: Learn about autofocus modes and manual focus. Practice achieving precise focus, especially for subjects with shallow depth of field.
In summary, delving into photography as a beginner requires grasping essential camera components: lenses, sensors, and settings. Take the time to experiment and learn how each element impacts your photos. Remember, practice is key, so don’t hesitate to explore and experiment to refine your photography skills.